Anatomy and physiology of brain and spinal cord pdf
Anatomy and physiology of brain and spinal cord pdf
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
6/09/2018 · BPK 448 2018-3 Rehabilitation of Movement Control J.A. Hoffer, Ph.D. Lecture 2 6 Sept 2018 Overview of Spinal Cord Anatomy and Physiology Introduction to Spinal Cord Injury This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology

Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
The spinal cord contains a number of sensory (ascending) pathways or tracts contained within the white matter. These pathways allow sensory information such as pain, touch, temperature or kinaesthesia (conscious proprioception) to be passed through the spinal cord and on to higher levels of the brain.
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has

KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
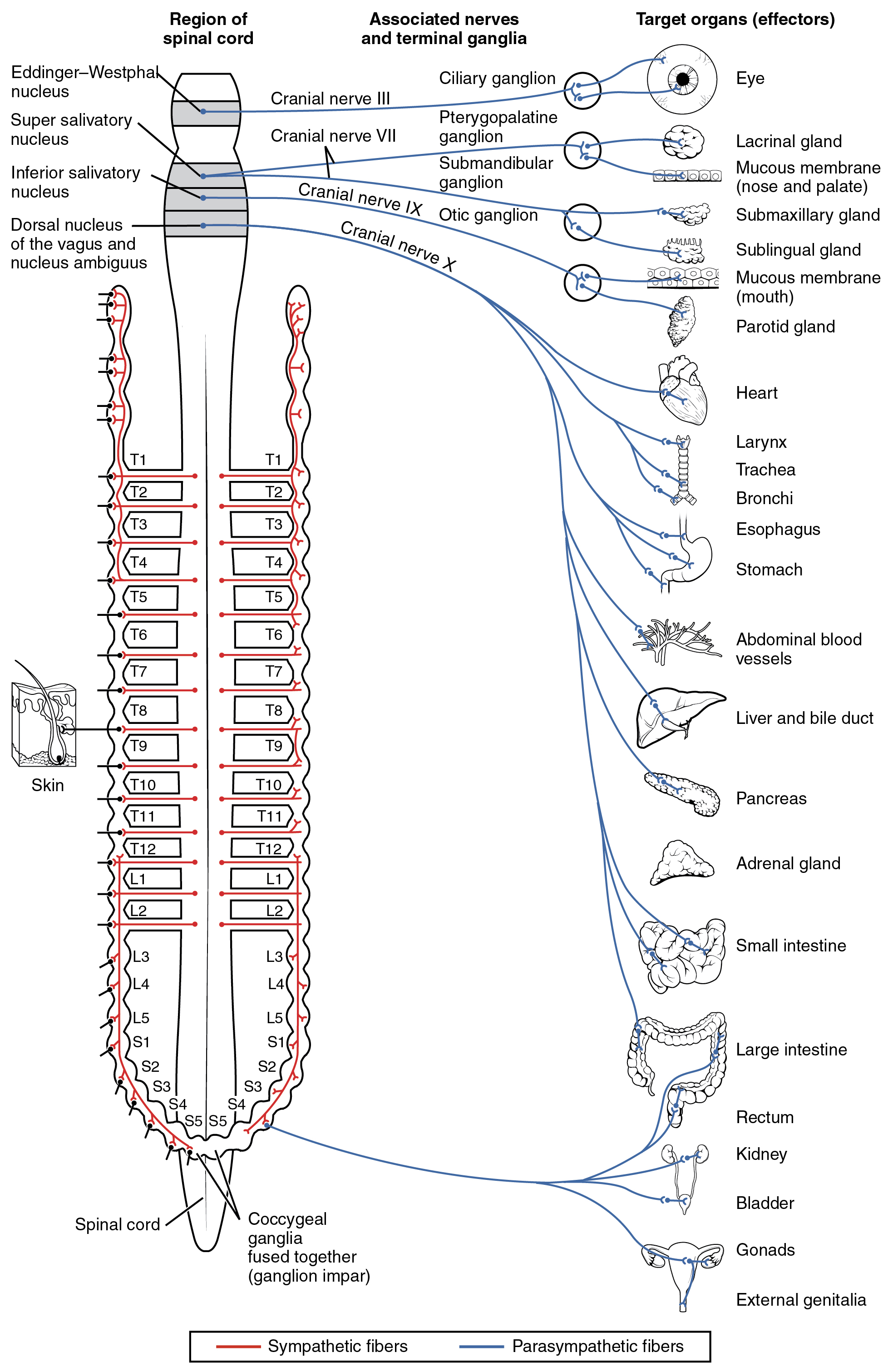
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
Request PDF on ResearchGate Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury The cellular elements and the chemical mediators in secondary injury following
Anatomy and Physiology The Spinal Cord. Delivering a Healthy WA Compiled by Jen Stayt, Spinal Patient Educator, Sir George Bedbrook Spinal Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, October 2007. Reviewed June 2009.. RPH M120730023 2 Causes of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by traumatic or non-traumatic injury. Many spinal cord injuries occur with fractures of the spinal …
Start studying Anatomy & Physiology: Brain & Spinal Cord. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits – statspin express 3 service manual
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink

BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body

The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube


–


Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
6/09/2018 · BPK 448 2018-3 Rehabilitation of Movement Control J.A. Hoffer, Ph.D. Lecture 2 6 Sept 2018 Overview of Spinal Cord Anatomy and Physiology Introduction to Spinal Cord Injury This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
Request PDF on ResearchGate Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury The cellular elements and the chemical mediators in secondary injury following
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
Request PDF on ResearchGate Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury The cellular elements and the chemical mediators in secondary injury following
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits
Start studying Anatomy & Physiology: Brain & Spinal Cord. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
Request PDF on ResearchGate Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury The cellular elements and the chemical mediators in secondary injury following
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
Start studying Anatomy & Physiology: Brain & Spinal Cord. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Anatomy and Physiology The Spinal Cord. Delivering a Healthy WA Compiled by Jen Stayt, Spinal Patient Educator, Sir George Bedbrook Spinal Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, October 2007. Reviewed June 2009.. RPH M120730023 2 Causes of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by traumatic or non-traumatic injury. Many spinal cord injuries occur with fractures of the spinal …
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
The spinal cord contains a number of sensory (ascending) pathways or tracts contained within the white matter. These pathways allow sensory information such as pain, touch, temperature or kinaesthesia (conscious proprioception) to be passed through the spinal cord and on to higher levels of the brain.
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
Anatomy and Physiology The Spinal Cord. Delivering a Healthy WA Compiled by Jen Stayt, Spinal Patient Educator, Sir George Bedbrook Spinal Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, October 2007. Reviewed June 2009.. RPH M120730023 2 Causes of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by traumatic or non-traumatic injury. Many spinal cord injuries occur with fractures of the spinal …
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits
Anatomy and Physiology The Spinal Cord. Delivering a Healthy WA Compiled by Jen Stayt, Spinal Patient Educator, Sir George Bedbrook Spinal Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, October 2007. Reviewed June 2009.. RPH M120730023 2 Causes of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by traumatic or non-traumatic injury. Many spinal cord injuries occur with fractures of the spinal …
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
Anatomy and Physiology The Spinal Cord. Delivering a Healthy WA Compiled by Jen Stayt, Spinal Patient Educator, Sir George Bedbrook Spinal Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, October 2007. Reviewed June 2009.. RPH M120730023 2 Causes of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by traumatic or non-traumatic injury. Many spinal cord injuries occur with fractures of the spinal …
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
Start studying Anatomy & Physiology: Brain & Spinal Cord. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
The spinal cord contains a number of sensory (ascending) pathways or tracts contained within the white matter. These pathways allow sensory information such as pain, touch, temperature or kinaesthesia (conscious proprioception) to be passed through the spinal cord and on to higher levels of the brain.
6/09/2018 · BPK 448 2018-3 Rehabilitation of Movement Control J.A. Hoffer, Ph.D. Lecture 2 6 Sept 2018 Overview of Spinal Cord Anatomy and Physiology Introduction to Spinal Cord Injury This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
Request PDF on ResearchGate Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury The cellular elements and the chemical mediators in secondary injury following
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
The spinal cord contains a number of sensory (ascending) pathways or tracts contained within the white matter. These pathways allow sensory information such as pain, touch, temperature or kinaesthesia (conscious proprioception) to be passed through the spinal cord and on to higher levels of the brain.
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
The spinal cord contains a number of sensory (ascending) pathways or tracts contained within the white matter. These pathways allow sensory information such as pain, touch, temperature or kinaesthesia (conscious proprioception) to be passed through the spinal cord and on to higher levels of the brain.
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25 Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
The spinal cord contains a number of sensory (ascending) pathways or tracts contained within the white matter. These pathways allow sensory information such as pain, touch, temperature or kinaesthesia (conscious proprioception) to be passed through the spinal cord and on to higher levels of the brain.
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
Request PDF on ResearchGate Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury The cellular elements and the chemical mediators in secondary injury following
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Anatomy and Physiology The Spinal Cord. Delivering a Healthy WA Compiled by Jen Stayt, Spinal Patient Educator, Sir George Bedbrook Spinal Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, October 2007. Reviewed June 2009.. RPH M120730023 2 Causes of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by traumatic or non-traumatic injury. Many spinal cord injuries occur with fractures of the spinal …
The spinal cord contains a number of sensory (ascending) pathways or tracts contained within the white matter. These pathways allow sensory information such as pain, touch, temperature or kinaesthesia (conscious proprioception) to be passed through the spinal cord and on to higher levels of the brain.
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
The spinal cord contains a number of sensory (ascending) pathways or tracts contained within the white matter. These pathways allow sensory information such as pain, touch, temperature or kinaesthesia (conscious proprioception) to be passed through the spinal cord and on to higher levels of the brain.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
Anatomy and Physiology The Spinal Cord. Delivering a Healthy WA Compiled by Jen Stayt, Spinal Patient Educator, Sir George Bedbrook Spinal Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, October 2007. Reviewed June 2009.. RPH M120730023 2 Causes of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by traumatic or non-traumatic injury. Many spinal cord injuries occur with fractures of the spinal …
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Anatomy and Physiology The Spinal Cord. Delivering a Healthy WA Compiled by Jen Stayt, Spinal Patient Educator, Sir George Bedbrook Spinal Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, October 2007. Reviewed June 2009.. RPH M120730023 2 Causes of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by traumatic or non-traumatic injury. Many spinal cord injuries occur with fractures of the spinal …
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Anatomy and Physiology The Spinal Cord. Delivering a Healthy WA Compiled by Jen Stayt, Spinal Patient Educator, Sir George Bedbrook Spinal Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, October 2007. Reviewed June 2009.. RPH M120730023 2 Causes of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by traumatic or non-traumatic injury. Many spinal cord injuries occur with fractures of the spinal …
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Request PDF on ResearchGate Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury The cellular elements and the chemical mediators in secondary injury following
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
The spinal cord contains a number of sensory (ascending) pathways or tracts contained within the white matter. These pathways allow sensory information such as pain, touch, temperature or kinaesthesia (conscious proprioception) to be passed through the spinal cord and on to higher levels of the brain.
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
The spinal cord contains a number of sensory (ascending) pathways or tracts contained within the white matter. These pathways allow sensory information such as pain, touch, temperature or kinaesthesia (conscious proprioception) to be passed through the spinal cord and on to higher levels of the brain.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Consists of nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain to other parts of the body such as muscles, intestines, and the skin . Cranial Nerves. Nerves that originate in the brain, There are 12. Autonomic Nervous System. Consists of nerves going to the various organs and smooth muscle which are involuntary in nature. Neuron. Basic Unit of the nervous system. Dendrites. Sensory projections
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Request PDF on ResearchGate Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury The cellular elements and the chemical mediators in secondary injury following
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Start studying Anatomy & Physiology: Brain & Spinal Cord. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
6/09/2018 · BPK 448 2018-3 Rehabilitation of Movement Control J.A. Hoffer, Ph.D. Lecture 2 6 Sept 2018 Overview of Spinal Cord Anatomy and Physiology Introduction to Spinal Cord Injury This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
6/09/2018 · BPK 448 2018-3 Rehabilitation of Movement Control J.A. Hoffer, Ph.D. Lecture 2 6 Sept 2018 Overview of Spinal Cord Anatomy and Physiology Introduction to Spinal Cord Injury This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy and Physiology The Spinal Cord. Delivering a Healthy WA Compiled by Jen Stayt, Spinal Patient Educator, Sir George Bedbrook Spinal Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, October 2007. Reviewed June 2009.. RPH M120730023 2 Causes of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by traumatic or non-traumatic injury. Many spinal cord injuries occur with fractures of the spinal …
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
6/09/2018 · BPK 448 2018-3 Rehabilitation of Movement Control J.A. Hoffer, Ph.D. Lecture 2 6 Sept 2018 Overview of Spinal Cord Anatomy and Physiology Introduction to Spinal Cord Injury This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord is free HD wallpaper. This wallpaper was upload at September 04, 2017 upload by admin in Head Anatomy.
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
Start studying Anatomy & Physiology: Brain & Spinal Cord. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Start studying Anatomy & Physiology: Brain & Spinal Cord. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
The spinal cord contains a number of sensory (ascending) pathways or tracts contained within the white matter. These pathways allow sensory information such as pain, touch, temperature or kinaesthesia (conscious proprioception) to be passed through the spinal cord and on to higher levels of the brain.
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
The brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column and by cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless fluid produced by the brain, which cushions the brain and spinal cord within the posterior (dorsal) cavity.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
•An interneuron with the cell body in the spinal cord or brain Anterior Spinal spinocerebellar cord tract Spinocerebellar tracts Posterior spinocerebellar tract Proprioceptive input from Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles, and joint capsules The spinocerebellar tracts carry proprioceptive information to the cerebellum. (Only one tract is detailed on each side, although each side has
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
Request PDF on ResearchGate Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury The cellular elements and the chemical mediators in secondary injury following
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Nógrádi A., Vrbová G. (2006) Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord. In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord. Neuroscience Intelligence Unit. Springer, Boston, MA In: Transplantation of Neural Tissue into the Spinal Cord.
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
6/09/2018 · BPK 448 2018-3 Rehabilitation of Movement Control J.A. Hoffer, Ph.D. Lecture 2 6 Sept 2018 Overview of Spinal Cord Anatomy and Physiology Introduction to Spinal Cord Injury This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
6/09/2018 · BPK 448 2018-3 Rehabilitation of Movement Control J.A. Hoffer, Ph.D. Lecture 2 6 Sept 2018 Overview of Spinal Cord Anatomy and Physiology Introduction to Spinal Cord Injury This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Request PDF on ResearchGate Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury The cellular elements and the chemical mediators in secondary injury following
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
“human heart anatomy and physiology pdf pictures, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf photos, human heart anatomy and physiology pdf image gallery” “This is a more advanced diagram of the heart. It labels all of the structures in a heart, and shows the unidirectional flow of blood.” “Heart” Nerf Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Chiropractic Adjustment Chiropractic Care Chiropractic Benefits
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Anatomy and Physiology The Spinal Cord. Delivering a Healthy WA Compiled by Jen Stayt, Spinal Patient Educator, Sir George Bedbrook Spinal Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, October 2007. Reviewed June 2009.. RPH M120730023 2 Causes of Spinal Cord Injury Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by traumatic or non-traumatic injury. Many spinal cord injuries occur with fractures of the spinal …
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
6/09/2018 · BPK 448 2018-3 Rehabilitation of Movement Control J.A. Hoffer, Ph.D. Lecture 2 6 Sept 2018 Overview of Spinal Cord Anatomy and Physiology Introduction to Spinal Cord Injury This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Spinal Cord • Together with brain forms the CNS • Functions – spinal cord reflexes – integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses – highway for upward and downward travel of sensory and motor information 3 Spinal Cord Protection •The spinal cord is protected by two connective tissue coverings, the meninges and vertebrae, and a cushion of cerebrospinal fluid
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
The Structure and Function of the Brain and Spinal Cord
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Exam lThere will be some questions on neurotransmitters and neuromodulators (most of these have been covered at different times through the brain and spinal cord (see various study guides) and also with nerve and muscle physiology (chapter 12) on exam 3.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
A. Spinal Cord Anatomy (p. 554) 1. Surrounding and protecting the delicate nervous tissue of the spinal cord (and, in a similar way, the brain) are: i.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Anatomy of the brain and spinal cord, with special reference to mechanism and function. By Harris E. Santee, M. D., Ph.D. Fourth edition, revised and enlarged.
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Brain and Spinal Cord Review YouTube
The spinal meninges surround the spinal cord and are continuous with the cranial meninges, which encircle the brain. The most superficial of the three spinal meninges is the the dura mater (which is latin for tough mother), is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy & Physiology Brain & Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy – See more about Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy, anatomy of brain and spinal cord pdf, brain and spinal cord anatomical drawings, brain
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink
Brain and Spinal Cord Human Anatomy and Physiology
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. typically specialize in a particular branch of physiology. For example, neurophysiology is the study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking. Physiologists may work from the organ level (exploring, for example, what
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
impulses travel from the spinal cord toward the brain (thalamus) and it’s found in the anterior part of the spinal cord. anterior spinothalamic tract automatic responses to changes in the environment.
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
(PDF) The Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord in
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Spinal Cord and Reflexes drcarman.info
Anatomy and physiology of the brain. and spinal cord The brain is a spongy organ made up of nerve and supportive tissues. It is located in the head and is
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
4 photos of the “Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord”
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Anatomy of the Spine Mayfield Brain & Spine
Motor Neurons Upper Motor Neurons • Found in corticospinal (or pyramidal tract) in brain/spinal cord Clinical Signs: 1. Loss of voluntary movement
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
21/10/2015 · Brain and Spinal Cord review video with terms! Thank you to Dr Kelly Wallace for contributing the knowledge and the demo for the video!
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Altered Cellular Anatomy and Physiology of Acute Brain
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 13- The Spinal Cord and
KEY POINTS • The spinal cord connects the brain neurologically with the body. The cord is enveloped within cerebrospinal fluid, and the pia, arachnoid and dural membranes, and anchored by
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
BPK 448 Lecture 2 Spinal Cord 6 Sept 2018.pdf BPK 448
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System; Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best 25+ Nervous System Ideas On Pinterest Nervous System
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain and Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is connected to the brain at the brainstem and is covered by the vertebrae of the spine. Nerves exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between the brain and the nerves in the rest of the body.
Spinal Cord Anatomy Human Anatomy – Lecture Notes – Docsity
Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Anatomy Inner Body
Start studying Anatomy & Physiology: Brain & Spinal Cord. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Best
The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord, and Spinal Nerves CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name the major subdivisions of the nervous system. 2. Classify the different types of neuroglia cells. 3. List the structural and functional classifi cation of neurons. 4. Explain how a neuron transmits a nerve impulse. 5. Name the different types of neural
Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord SpringerLink